Search Results for: air cell
Ethmoid air cells
Definition noun The numerous tiny-walled, fluid-filled cells that lie in the ethmoid bone of the skull (i.e. specifically... Read More
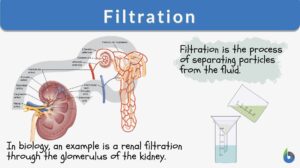
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
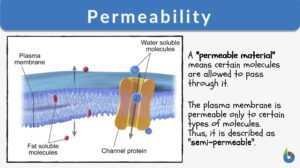
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Biological Viruses
The prime directive of all organisms is to reproduce and survive and this also applies to viruses. Apparently, viruses are... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction Definition What is asexual reproduction? Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Law of biogenesis
Law Of Biogenesis Definition Law of Biogenesis states that life arises from pre-existing life, not from nonliving matter.... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More